Synthetic Biology: market drivers, challenges and R&D oppo...
Synthetic biology (or SynBio) is an exciting intersection of biology and engineering, which promi...

Small and Medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)are the lifeblood of innovation in the UK. We’ve dived into the most recent SME statistics, exploring their contribution to the UK economy.
According to the Business population estimates for the UK and regions 2023, there are 5.51 million SMEs, which make up 99.9% of UK private sector businesses. 5.51 million of these are classed as “small” (0 to 49 employees) and 36,905 are classed as “medium-sized” (50 to 249 employees).
There are a further 4,060 businesses that could potentially be classed as SMEs for R&D Tax Credits purposes as they employ between 250 to 499 people (if they fulfil the rest of the criteria – see below).
While reporting the number of SMEs in the UK, the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy uses the basic criteria of between 0 to 49 employees for a small business and 50 to 249 employees for a medium-sized business.
For applying for R&D Tax Credits, the definition of an SME in the UK is more specific. The SME R&D scheme defines Small and Medium-sized enterprises as having a headcount below 500 and a turnover of under €100m, or a balance sheet that totals less than €86m (regardless of the number of employees). There are several rules that might prevent an SME from applying through the SME scheme, such as if the company’s R&D is subsidised, or if they are conducting R&D as subcontractors. Under these circumstances, SMEs would apply for tax relief under the RDEC scheme.
The process becomes simpler for accounting periods starting on or after 1 April 2024, when SMEs must apply for R&D relief through a new single scheme that merges both the SME scheme and RDEC (except when they are classed as being an “R&D intensive” SME, which means that the business’s R&D spend makes up 30% of their total expenditure).
You can read about the full criteria for qualifying as an SME for tax relief on our SME scheme page.
The government’s statistics show that in 2023 SMEs employed 16.7 million people in the UK, 61% of the total number of people employed by private sector companies.
The government reports that turnover for UK SMEs was £2.4 trillion in 2023, 53% of the total turnover of private businesses.
For the 2021-2022 tax year, HMRC estimates that 85,625 Small or Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) made R&D claims, 95% of all claims.
79,205 of these made SME scheme claims, which break down as:
As well as this, there were 6,420 SMEs that claimed under the RDEC scheme.
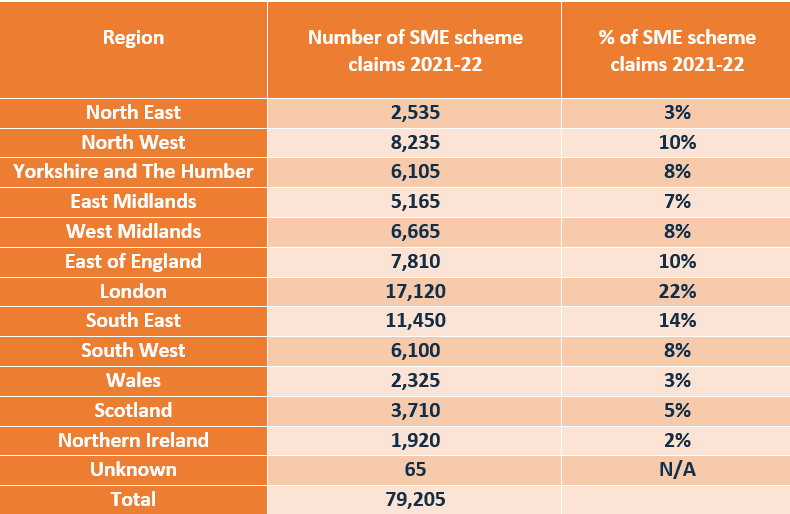
For the 2021-22 tax year, 90% of businesses who made SME R&D Tax Credits scheme claims were from England. 3% were from Wales. 5% were from Scotland and 2% were from Northern Ireland.
22% of SME scheme claims came from London, 14% came from the South East and 10% came from the North West and another 10% from the East of England. The table below shows the number and percentage share of SMEs claiming R&D Tax Credits, broken down by region for the most recent tax year.
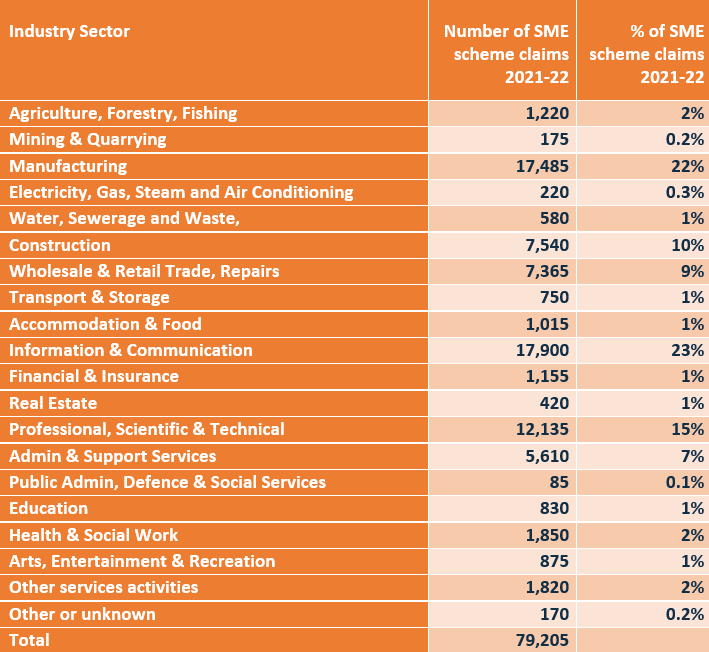
For the 2021-22 tax year, the majority of SME R&D Tax Credits scheme claims came from just three industries, including Information & Communication (23%), Manufacturing (22%) and Professional, Scientific & Technical (15%).
The table below shows the number and percentage share of SMEs claiming R&D Tax Credits, broken down by industry for the most recent tax year.
According to the government’s Longitudinal Small Business Survey: SME Employers – UK, 2022, 52% of SMEs have women in management roles. This figure breaks down as:
The industries most likely to be led by women are Health (44%), Education (34%), Other Services (29%) and Food & Accommodation (28%).
The government’s Small Business Survey reported that 6% of SMEs were led by a management team with at least half of its members from minority ethnic groups. The industries most likely to be led by members from ethnic minority groups are Information & Communication (9%), Health (8%), Food & Accommodation (8%), Education (8%) and Admin (8%).
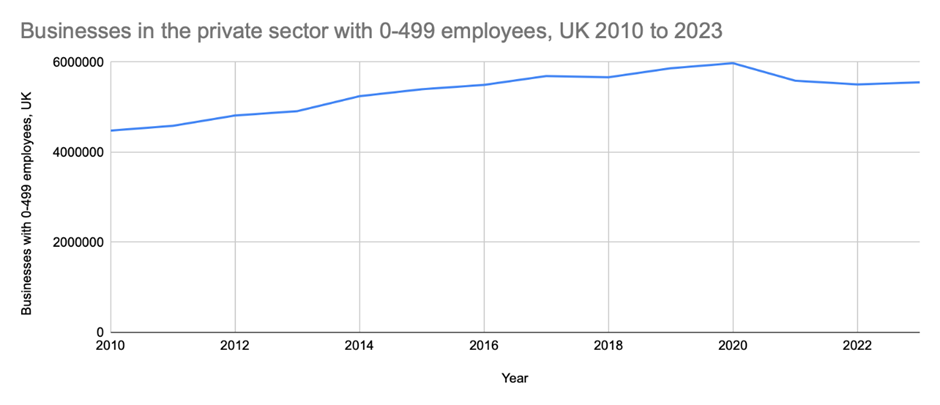
For nearly twenty years, there has been sustained growth in the number of businesses in the private sector with 0-499 employees; however, according to the latest HMRC data, the number of SMEs declined from 2021 to 2022, with growth starting to return in 2023. In the table below we show growth of UK SMEs in the private sector from 2010 to 2023.
We don’t have the full data from the 2021-22 tax year; however, we know that in the tax year 2020-21, there was a 3% decrease in the overall number of first-time applicants from the previous year.
The table below shows the number of first-time R&D Tax Credits claimants from 2000-01 to 2021-22.
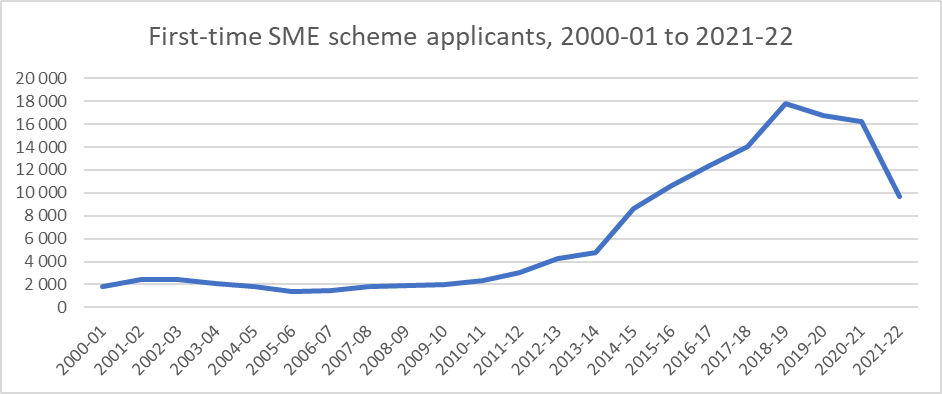
Note: the number of first-time SME scheme applications for 2021-22 is only partial and will be revised by HMRC at a later date.
In the 2022 Small Business Survey, SMEs reported the following obstacles to growth:
The 2022 Small Business Survey reported that around three-quarters of SMEs (75%) use some form of external finance. This is up from 74% in 2021, 72% in 2020 and 63% in 2019.
According to the government’s 2022 SME Survey:
While many of these innovations just took place within their respective businesses, of the SMEs that innovated new processes, 19% were new to the industry. Of the SMEs that innovated goods or services, 31% were new to the industry or market. Goods and services innovations new to the industry or market were most likely to come from Construction, (42%), Manufacturing (42%) or Information & Communications (51%).
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like:
Explore our latest insights

Synthetic biology (or SynBio) is an exciting intersection of biology and engineering, which promi...

Even in the best of circumstances, we know that it can be challenging to balance a successful car...

Full expensing is a first-year allowance that allows businesses to reduce their tax liability and...

To help businesses understand if their work qualifies for R&D Tax Relief and to make sure tha...